16th Century German map of Marburg /Kassel G BRAUN /F HOGENBERG Civitatus Orbis








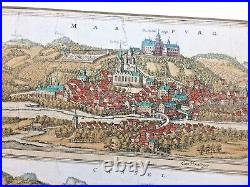



16th Century birds eye map of Marburg / Kassel Marpurg / Cassel created by George Braun. Flemish / German engraver and mapmaker. This map was designed to be part of Civitatus Orbis Terrarum the most important book of town plans and views published in the 16th Century and is a later engraving probably 1657.
Size 58 cm x 47 cm. CARTOUCHE: Marburg, capital of Hesse, distinguished for its university.
On top of a high hill is the residence of the Prince, with a chapel built by Louis, bishop of Münster, third son of Landgrave Henry of Thuringia. There is also a university here in which the liberal arts are taught, founded in 1527 and renewed in 1535 by Prince Philip. In this view of Marburg from the east, the city's two most familiar buildings are seen to advantage: the palace on top of the hill (centre), where a castle had first been built in the 9th century, and St Elizabeth's church (in front of it on the left). Marburg only assumed importance from 1228, when Elizabeth of Thuringa settled here and began her selfless mission tending the poor and sick. In 1235, just four years after her death, she was canonized and the Teutonic Order embarked on the construction of the early Gothic church of St Elizabeth. Due to the pilgrims who came from all over Europe to visit Elizabeth's tomb, Marburg's ecocomy flourished. In 1539, however, wishing to halt this pilgrimage, the Protestant landgrave Philip the Magnanimous of Hesse-Marburg had Elizabeth's bones removed from the church. Taschen, Braun and Hogenberg, p.CARTOUCHE: Cassula, commonly known as Kassel, a flourishing town in wool-producing Hesse, strongly fortified by moats, a citadel and bulwarks; called Stereontium by Ptolemy. Kassel, the noblest town in Hesse, so called on account of its fortified castle; for formerly, it is said, only a palace stood there. The Rivers Fulda, Ahne and Drusel flow through Kassel, hence the city has a fertile soil. Its most important commodities are cattle, animal hides and wool.
They sell these wares, in particular wool, partly to Buvonia, which lies close to the land of Thuringia, partly within their native land, and they also take it to the famous mercantile city of Antwerp and from there to London. In the centre of the picture is St Martin's church, dating from the 14th/15th centuries; the soaring south tower was given its octagonal turret and Italian cupola as late as the 16th century.In the left-hand foreground, on the other side of the Fulda, are the grounds of the Neuer Lustgarten, the forerunner of the present Fuldaaue park, which together with the Karlsaue and the hillside Wilhelmshöhe Berg numbers amongst modern-day Kassel's spacious parks and gardens. First mentioned in records in AD 913, the town evolved out of a castle, from which it also derives its name.
From 1277 Kassel - in alternation with Marburg - was the capital of Hesse.